About PhenoSV
PhenoSV is a phenotype-aware machine-learning model to interpret all types of structural variants (SVs) that disrupt either coding or noncoding genome regions, including deletions, duplications, insertions, inversions, and translocations. When phenotype information is available, PhenoSV further utilizes gene-phenotype associations to prioritize disease-related SVs.
On this website, you can score a single SV that affects less than 10 genes or upload a file to score multiple SVs (<10 SVs). We suggest to download PhenoSV and run offline for more computational intensive tasks.
General Usage
The navigation bar provides options to score a single SV (deletion, duplication, insertion, inversion), score multiple SVs, or score a translocation.
The default genome build is GRCh38. We can also choose GRCh37.


Score a single SV
For a single SV that is deletion, duplication, insertion, or inversion, you need to select required fields for the SV.
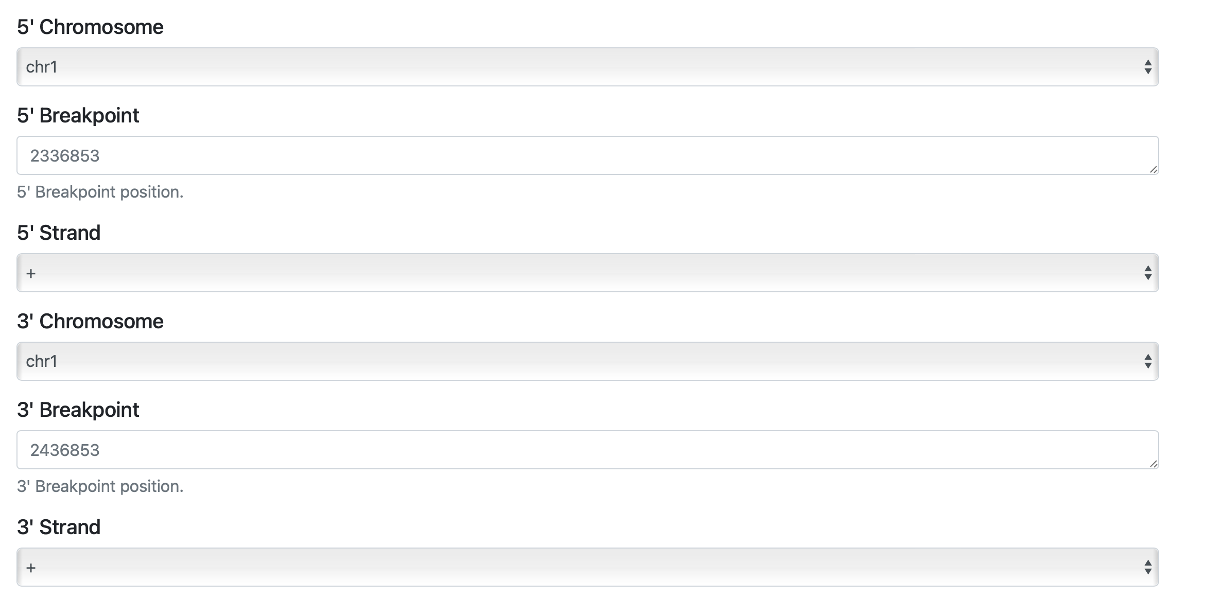
For a single SV that is translocation, you need to select required fields as shown below.
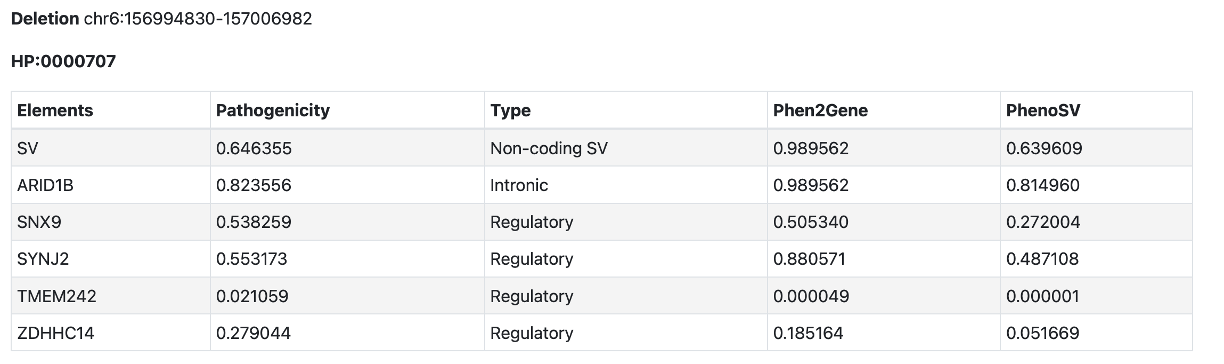
You can enter available phenotype information using HPO terms to score disease-related SV. PhenoSV will utilize gene-phenotype relationships to refine PhenoSV scores. HPO terms can be a list and should in the format of HP:digits, e.g., HP:0000707, separated by semicolons, newlines, commas, or spaces. Below is a sample output. Column Pathogenicity represents general pathogenicity of overall SV and each gene impacted. Column Phen2Gene represents gene-phenotype relationships (percentile of Pheno2Gene score). Column PhenoSV is refined PhenoSV scores given prior phenotype information.
Values of α controls the degree of using gene-phenotype associations in refining PhenoSV scores. α should be a positive value, whereas larger values representing higher impacts of phenotype information referred in PhenoSV scoring, and vise versa.
Choose inference mode to "full mode" if you want to infer the indirect impact of coding SVs on distal genes in addition to their direct impacts on genes covered.
Choose inference scope from 'distance' and 'tad'. When choosing 'distance', genes within 1Mbp distance to the noncoding SVs will be considered. When choosing 'tad', genes within TAD will be considered. A consensus TAD annotation is used.

Score multiple SVs
csv, bed, and bedpe (translocation) files containing multiple SVs can be uploaded and score together. We will only score the first 10 SVs. For more SVs, please use the command-line tool and score them offline. Sample input files can be found here.
For BED and CSV files, columns should be in the order of chromosome (e.g., chr1), start, end, ID, SV types (e.g., deletion, duplication, insertion, inversion), and HPO terms (optional). Below is an example.
BEDPE files can be used to interpret translocations. Columns should be in the order of chromosome1 (e.g., chr1), start1 (breakpoint1), end1 (placeholder), chromosome2, start2 (breakpoint2), end2 (placeholder), strand1, strand2, ID, and HPO terms (optional). Below is an example.